In recent years, the soaring cost of higher education has become a global concern. With tuition fees at some top-ranked universities reaching astronomical levels, students and parents alike often wonder if it’s possible to obtain a world-class education without incurring crippling debt. This concern raises an important question: Can you get a world-class education at an affordable university?
The answer is a resounding yes. Around the globe, numerous affordable universities offer education that rivals the world’s best in quality, innovation, and outcomes. These institutions combine strong academic programs, respected faculty, robust research initiatives, and vibrant campus life—all while maintaining lower tuition and living costs.
This article explores the landscape of affordable higher education and identifies factors that define a “world-class” university. It also highlights notable affordable universities, how to evaluate them, and tips for maximizing your educational investment.
Key Takeaways
- World-class education is defined by quality of faculty, research, academic programs, and graduate outcomes—not just brand name.
- Tuition and living costs vary widely worldwide; several countries offer affordable yet prestigious education options.
- Accreditation and international recognition are critical when selecting affordable universities.
- Many affordable universities have strong research programs and active industry collaborations.
- Scholarships and financial aid play a significant role in making education affordable.
- Students should consider campus life, support services, and opportunities for personal development.
- Technology and online learning continue to expand access to affordable quality education.
Defining a World-Class Education
When discussing whether one can get a world-class education at an affordable university, it’s essential first to understand what “world-class education” actually means. The phrase often conjures images of prestigious, elite institutions with long histories and global name recognition. However, a true world-class education goes far beyond branding and reputation. It encompasses several critical attributes that define the quality, impact, and value of the educational experience.
Academic Excellence and Rigor
At its core, a world-class education is marked by academic excellence. This means the institution delivers a curriculum that is both comprehensive and challenging, designed to push students to develop critical thinking, creativity, and problem-solving skills. The academic programs should be:
- Well-structured and up to date: Curricula must reflect the latest developments in each field, integrating emerging knowledge, technologies, and methodologies.
- Balanced theory and practice: Students should gain not only foundational theoretical knowledge but also practical skills through labs, projects, internships, and experiential learning.
- Interdisciplinary: Modern challenges often require knowledge across multiple disciplines. World-class institutions encourage cross-disciplinary study and collaboration.
Distinguished Faculty
A hallmark of a world-class education is the quality of its faculty. Leading universities attract and retain top scholars, researchers, and practitioners who are experts in their fields. These professors are not only effective teachers but also active contributors to advancing knowledge through research. Features include:
- Expertise and credentials: Faculty members with advanced degrees, significant publications, and professional recognition (Nobel laureates, Fields Medalists, etc.).
- Innovative teaching methods: Professors who employ active learning, technology integration, and mentorship to enhance student engagement.
- Research leadership: Faculty who are pioneering discoveries and driving innovation that impacts society.
Research and Innovation
Research is a critical pillar of a world-class education. Universities that contribute significantly to advancing knowledge, technology, and society provide students with unique opportunities to participate in groundbreaking projects. This not only enriches learning but also enhances the university’s global standing. Key elements include:
- Research output: Publications in high-impact journals, patents, and contributions to major scientific and technological breakthroughs.
- Research facilities: Access to state-of-the-art labs, libraries, and technology centers that support cutting-edge work.
- Student involvement: Opportunities for undergraduate and graduate students to engage in research projects, fostering a culture of inquiry.
Global Recognition and Accreditation
Being recognized globally by peers, employers, and accreditation bodies ensures that an institution’s education standards meet rigorous international benchmarks. Accreditation serves as quality assurance and adds credibility to degrees. Characteristics include:
- International accreditations: From organizations such as ABET (engineering), AACSB (business), or regional accreditation agencies.
- High global rankings: Recognition in established university rankings (QS, Times Higher Education, Shanghai Ranking) reflects quality across multiple indicators.
- Alumni success: Graduates who excel globally in academia, industry, government, and arts reinforce the university’s reputation.
Comprehensive Student Development
A world-class education extends beyond academics to develop well-rounded individuals ready to thrive in diverse environments. This includes fostering:
- Critical soft skills: Communication, leadership, teamwork, and ethical reasoning are emphasized alongside technical knowledge.
- Cultural competence: Exposure to diverse perspectives through international students, study abroad, and inclusive campus culture.
- Personal growth: Encouraging students to develop resilience, creativity, and lifelong learning habits.
Employability and Career Outcomes
Ultimately, a world-class education prepares students for successful careers and societal contribution. Institutions measure their success by how well graduates perform in the job market and their impact on their fields. Indicators include:
- High graduate employment rates: Alumni working in respected positions across industries and sectors worldwide.
- Strong industry connections: Partnerships that facilitate internships, cooperative education, and job placement.
- Entrepreneurship and innovation: Support for startups and ventures initiated by students and alumni.
Vibrant Campus Life and Support Systems
The environment in which students learn plays a vital role in the educational experience. World-class universities provide rich campus life that nurtures intellectual curiosity, social engagement, and wellbeing, through:
- Diverse student organizations: Clubs, societies, and activities catering to academic, cultural, and recreational interests.
- Support services: Academic advising, mental health counseling, career centers, and inclusion programs.
- Facilities and infrastructure: Modern classrooms, libraries, housing, and technology resources to support learning and community.
Commitment to Social Impact and Global Challenges
Leading universities take on the responsibility of addressing pressing societal issues through education, research, and outreach. Their work contributes to sustainable development, health advancements, equity, and peace-building globally. Students are encouraged to engage with these challenges, cultivating a sense of purpose and responsibility.
The Rising Cost of Higher Education Globally
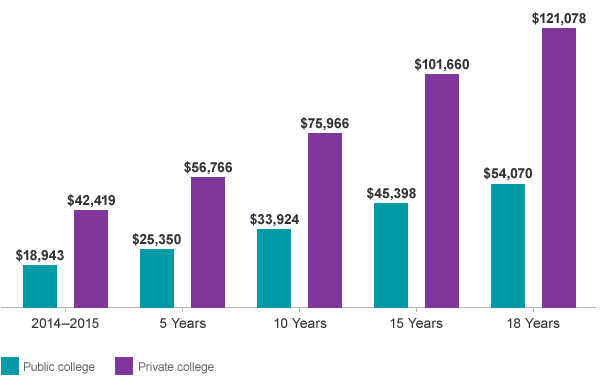
In recent decades, the cost of higher education has escalated dramatically around the world, making it increasingly difficult for many students and families to afford quality postsecondary education. This trend has sparked debates on accessibility, student debt, and the value of higher education, raising important questions about who can truly benefit from a world-class education.
Trends in Tuition Fee Increases
The most visible factor contributing to the rising cost of higher education is the steady increase in tuition fees. In many countries, tuition has grown at rates far outpacing inflation and wage growth, placing substantial financial burdens on students.
- United States: Over the past 30 years, tuition and fees at public universities have more than tripled, while private university costs have also seen sharp increases. For example, the average annual tuition at public four-year institutions rose from around $2,000 in the early 1990s to over $10,000 today (adjusted for inflation).
- United Kingdom: Tuition fees increased from approximately £1,000 per year in the 1990s to a cap of £9,250 per year for home students in recent years.
- Australia, Canada, and New Zealand: These countries have also witnessed significant tuition fee growth, particularly for international students, who often pay two to three times more than domestic students.
- Developing countries: Even in emerging economies, where public education was traditionally subsidized, tuition fees have risen due to reduced government funding and increasing demand.
Factors Driving Cost Increases
Several factors have contributed to the rising cost of higher education:
- Reduced public funding: Many governments have cut subsidies for universities, shifting more of the financial burden to students through tuition hikes.
- Expanded campus services: Universities have invested heavily in infrastructure, technology, student amenities, and administrative services, which add to operating costs.
- Increased demand: Growing numbers of students seeking higher education have put pressure on universities to expand facilities and programs.
- Research costs: High-quality research requires significant investment in laboratories, equipment, and personnel.
- Competitive market: Universities compete for top faculty, students, and rankings, leading to increased spending on marketing, scholarships, and facilities.
The Impact on Students and Families
The rising cost of education affects students and their families in multiple ways:
- Student debt crisis: In countries like the U.S., students graduate with average debt burdens exceeding $30,000, leading to long-term financial strain and delayed milestones such as buying a home or starting a family.
- Access and equity issues: High costs deter many capable students, especially from low- and middle-income families, from pursuing higher education. This exacerbates social inequality and limits social mobility.
- Mental health consequences: Financial stress contributes to anxiety, depression, and other mental health challenges among students.
- Influence on career choices: Students burdened with debt may choose higher-paying jobs over their passions or social-impact careers.
The Cost Divide: Elite vs. Affordable Universities
While the most prestigious universities command the highest tuition fees, there is a growing divide in cost and accessibility among global institutions:
- Elite universities: Ivy League schools, Oxbridge, and other top-tier institutions often charge premium tuition, supported by wealthy endowments and offering extensive resources and networking opportunities.
- Affordable universities: Many institutions, particularly public universities in countries with strong education subsidies or lower costs of living, offer world-class programs at a fraction of the cost. Examples include German public universities, Scandinavian institutions, and some Asian universities.
The Role of Scholarships and Financial Aid
To mitigate the rising costs, many universities and governments provide scholarships, grants, and financial aid. However, these resources are often limited and highly competitive. Additionally, the complexity of applying for aid and varying eligibility criteria can make accessing these funds challenging for many students.
The Global Variation in Education Costs
Education costs vary widely worldwide, influenced by economic conditions, government policies, and cultural priorities:
- Germany and Nordic countries: Many offer tuition-free or low-cost education to both domestic and international students, focusing on accessibility and equity.
- United States: High tuition fees combined with a large private university sector lead to the highest education costs globally.
- Asia: Countries like China, Japan, and South Korea have moderate tuition fees but growing demand is pushing costs upward.
- Africa and Latin America: Many countries still rely heavily on public funding to keep tuition low, though quality and access remain challenges.
Alternatives and Innovations to Combat Costs
To address affordability, the education sector is witnessing innovations such as:
- Online education: Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs) and fully online degree programs reduce costs and increase access.
- Competency-based education: Students progress based on skills mastery rather than time, potentially shortening degree durations and lowering expenses.
- Income share agreements: Some institutions offer funding models where students repay tuition as a percentage of future income, reducing upfront costs.
- Policy reforms: Governments are reconsidering funding models to balance quality and access.
Affordable Universities: What Does ‘Affordable’ Mean?
- Defining affordability (tuition, living costs, scholarships)
- Geographic factors influencing affordability
- Examples of countries with affordable higher education (Germany, Norway, Canada, etc.)
- Private vs public affordable universities
Examples of Affordable Universities Offering World-Class Education
- University of Warsaw, Poland
- University of Cape Town, South Africa
- National University of Singapore (NUS) (moderate fees, world-class quality)
- University of Buenos Aires, Argentina
- Technical University of Munich, Germany
- University of British Columbia, Canada
- University of São Paulo, Brazil
Detailed profiles: programs offered, research output, rankings, tuition fees
Factors to Evaluate When Choosing an Affordable University
- Accreditation and global recognition
- Academic programs and faculty credentials
- Research facilities and innovation hubs
- Career support and alumni network
- Student satisfaction and campus life
- International student support and exchange programs
How to Maximize Your Educational Experience at an Affordable University
- Leveraging scholarships and financial aid
- Engaging in research and internships
- Networking and building professional connections
- Utilizing online resources and continuing education
- Participating in extracurricular activities and leadership opportunities
Challenges and Limitations of Affordable Universities
- Language barriers and cultural adjustments
- Resource constraints and infrastructure
- Competition with elite private universities
- How students can overcome these challenges
The Future of Affordable World-Class Education
- The role of technology and online education in affordability
- Government policies supporting affordable Education
- The growing importance of international collaborations
- Trends in university rankings and quality assessments
Also Read : What Jobs Can You Get with a Business Degree Today?
Conclusion
Obtaining a world-class education at an affordable university is not just possible but increasingly common. The global education landscape is evolving, with numerous institutions offering high-quality academic programs at a fraction of the cost of elite universities. By carefully evaluating universities based on accreditation, academic rigor, research output, and student support, prospective students can find excellent opportunities to thrive academically and professionally.
Affordability no longer means compromising quality. Instead, it reflects smart choices, strategic planning, and leveraging available resources to maximize educational outcomes. As education becomes more accessible worldwide, students from diverse backgrounds can pursue their dreams without the financial burdens historically associated with top-tier universities.
FAQs
Can affordable universities compete with elite universities in terms of quality?
Yes. Many affordable universities offer excellent faculty, research, and global partnerships, enabling them to provide a quality education comparable to elite institutions.
How can I find scholarships for affordable universities?
Most universities have scholarship programs based on merit, financial need, or specific fields of study. Research university websites and external scholarship databases for options.
Are degrees from affordable universities recognized internationally?
Many affordable universities are accredited and recognized globally, especially those listed in international rankings and part of global academic networks.
Is language a barrier at affordable universities?
While some universities teach in local languages, many affordable universities offer programs in English or other widely spoken languages, especially at the postgraduate level.
How do affordable universities support international students?
Affordable universities often provide dedicated international student offices, orientation programs, language support, and cultural integration activities.
Can I pursue research opportunities at affordable universities?
Yes, many affordable universities have strong research programs and encourage student participation in cutting-edge projects.
What are the living costs like when studying at affordable universities?
Living costs vary by country and city but are generally lower at affordable universities compared to those in expensive urban centers like New York or London.


